Servili, M.; Sordini, B.; Esposto, S.; Urbani, S.; Veneziani, G.; Di Maio, I.; Selvaggini, R.; Taticchi, A. Biological Activities of Phenolic Compounds of Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Antioxidants 2014, 3, 1-23.
Abstract
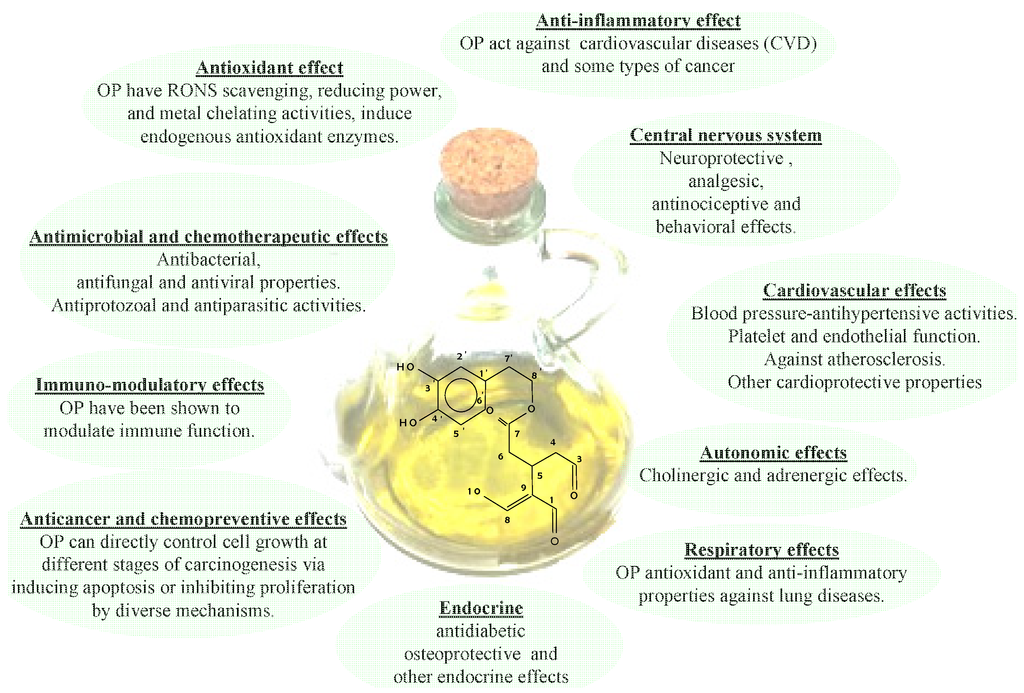
Over the last few decades, multiple biological properties, providing antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, chemopreventive and anti-cancer benefits, as well as the characteristic pungent and bitter taste, have been attributed to Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) phenols. In particular, growing efforts have been devoted to the study of the antioxidants of EVOO, due to their importance from health, biological and sensory points of view. Hydrophilic and lipophilic phenols represent the main antioxidants of EVOO, and they include a large variety of compounds. Among them, the most concentrated phenols are lignans and secoiridoids, with the latter found exclusively in the Oleaceae family, of which the drupe is the only edible fruit. In recent years, therefore, we have tackled the study of the main properties of phenols, including the relationships between their biological activity and the related chemical structure. This review, in fact, focuses on the phenolic compounds of EVOO, and, in particular, on their biological properties, sensory aspects and antioxidant capacity, with a particular emphasis on the extension of the product shelf-life.
Conclusions
The EVOO quality is intimately affected by its content in phenolic compounds. In fact, the hydrophilic phenols influence not only its shelf-life but also its health and sensory proprieties.
The review has been focused on the evaluation of the antioxidant effects of OPs. In particular, the antioxidant activities and healthy properties of secoiridoids derivatives, such as 3,4-DHPEA, 3,4-DHPEA-EDA, 3,4-DHPEA-EA, p-HPEA, p-HPEAEDA and lignans, have been taken into account. It was found that the high resistance to oxidation of EVOO is due to oleuropein and 3,4-DHPEA-EA derivatives, while lignans play a secondary role. Moreover, with respect to the healthy properties, these substances show a high antioxidant activity and play a key role in the prevention and/or reduction of chronic degenerative events based on inflammatory processes and chronic-degenerative diseases, such as cardiovascular-cerebral diseases and cancer. Furthermore, it was also found that the sensory notes of EVOO are affected by OPs. In fact, it was demonstrated that open ring p-HPEA-EDA is responsible for the strong “pungent” attribute, while closed ring 3,4-DHPEA-EA and p-HPEA-EA represent the impact components for the “bitter” note. The 3,4-DHPEA-EDA, which contributes to the sensation of bitter however, plays a marginal role for the “pungent” note.
In recent years, the innovation process in the field of EVOO is being orienting towards a new concept of quality, strictly related to OPs content (which, more than other compounds, are affected by technological processes) to end of producing EVOOs characterized by a strong sensory impact and healthy benefits.
See more at:
Nenhum comentário:
Postar um comentário